Auto Immune and Inflammatory Conditions
Currently, autoimmune conditions are treated with immune suppressive agents such as steroids, methothrexate, cyclosporine, gold, and more recently infliximab (Remicade). Despite inducing temporary improvement, these approaches possess the possibility of long-term adverse effects, as well as need for life-long treatment.
Stem cell therapy has been demonstrated to induce profound healing activity in animals with various forms of autoimmune disorders. Besides healing damaged tissues, stem cells have the unique ability to modulate the immune system so as to shut off pathological responses while preserving its ability to fight off disease. Stem cells and specifically, mesenchymal stem cells home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. These mediators act locally and do not suppress the immune response of the patient’s whole body. Additionally, mesenchymal stem cells induce the production of T regulatory cells, a type of immune cell whose function is to protect the body against immunological self-attack.
-

Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a valuable source for the treatment of immune-mediated disorders
-
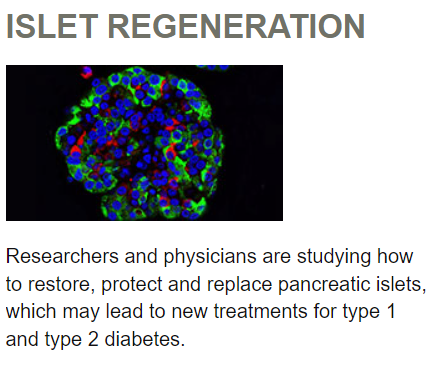
Stem cells may help replace missing or damaged beta cells, special cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes involve problems with beta cells (either there are not enough — or any — beta cells or the cells don’t function properly). Stem cell therapy might be helpful in patients with either type.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Perianal Crohn’s Disease
-
Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Lyme Disease
-
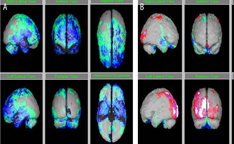
Single-photon emission tomography imaging in patients with Lyme disease treated with human embryonic stem cells
-

Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Severe and Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: 4 Years of Experience
-

Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of psoriasis: a comprehensive review
-
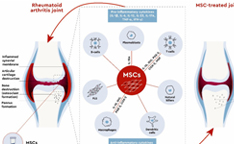
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects our joints. Stem cell therapy can help by repairing damaged joint cartilage and by reducing inflammation that occurs in and around the joint.
-

Fibromyalgia
Stem cells can be very helpful in modulating inflammatory responses, including inflammation thought to be associated with fibromyalgia. They can also help repair and regenerate damaged nerve cells that can “misfire,” sending pain signals when there is no painful stimulus



